Universal Allow/Block Prefs
The allow/block feature enables your app to request and respect user consent preferences. With this feature, another blockchain account address registered on the XMTP network can have one of three consent preference values:
- Unknown
- Allowed
- Denied
These values express a user's consent preferences for a contact. These consent preferences are stored privately in an encrypted consent list on the XMTP network. The consent list is accessible by all apps that a user has authorized.
Understand user consent preferences
Here are some of the ways user consent preferences are set:
Unknown
Conversation created in an app on an SDK version with user consent support:
- For a new conversation that a peer contact wants to start with a user, the consent preference is set to
unknown.
Conversation created in an app on an SDK version without user consent support:
- For all conversations with any peer contact, the consent preference is set to
unknown.
Allowed
Conversation created in an app on an SDK version with user consent support:
For a new conversation that a user created with a peer contact, the SDK sets the consent preference to
allowed.The user’s creation of the conversation with the contact is considered consent.
For an existing conversation created by a peer contact that hasn’t had its consent preference updated on the network (
unknown) and that the user responds to, the SDK will update the consent preference toallowed.The user's response to the conversation is considered consent.
For a peer contact that a user has taken the action to allow, subscribe to, or enable notifications from, for example, the app must update the consent preference to
allowed.
Conversation created in an app on an SDK version without user consent support:
- There are no scenarios in which a user consent preference will be set to
allowed.
Denied
Conversation created in an app on an SDK version with user consent support:
- For a peer contact that a user has taken the action to block, unsubscribe from, or disable notifications from, for example, the app must update the consent preference to
denied.
Conversation created in an app on an SDK version without user consent support:
- There are no scenarios in which a user consent preference will be set to
denied.
Use consent preferences to respect user intent
Your app should aim to handle consent preferences appropriately because they are an expression of user intent.
For example, if a user blocked a contact, your app should respect the user's intent to not see messages from the blocked contact. Handling the consent preference incorrectly and showing the user messages from the blocked contact may cause the user to lose trust in your app.
Be sure to load the latest consent list from the network at appropriate steps in your app flow to ensure that your app can operate using the latest data.
Here are some suggestions for how your app might provide user experiences that respect user intent based on consent preferences:
Unknown
Consider displaying a conversation with an unknown contact on a Requests tab and give the user the option to block or allow the contact.
Allowed
Consider displaying a conversation with an allowed contact on a Messages tab and give the user the option to block the contact.
Denied
Consider removing a conversation with a denied contact from the user’s inbox completely. In an appropriate location in your app, give the user the option to unblock the contact.
Enable user consent preferences
Use the following methods to enable user consent preferences in your app.
Deny or allow a contact
To enable your user to deny or allow a contact, call the following methods. Note that these functions accept lists, so you can do batch requests.
- JavaScript
- React
- Kotlin
- Swift
- Dart
- React Native
// from the client
await client.contacts.allow([address1, address2]);
await client.contacts.deny([address1, address2]);
// from a conversation
await conversation.allow();
await conversation.deny();
import { useConsent } from "@xmtp/react-sdk";
function ConsentControl({ conversation }) {
const { allow, deny } = useConsent();
const handleAllow = async () => {
await allow([conversation.peerAddress]);
// Additional UI logic or state updates after allowing
};
const handleDeny = async () => {
await deny([conversation.peerAddress]);
// Additional UI logic or state updates after denying
};
return (
// ... UI elements that call handleAllow and handleDeny
);
}
client.contacts.allow([wantedConvo.peerAddress, wantedConvo.peerAddress])
client.contacts.deny([spamConvo.peerAddress, unwantedConvo.peerAddress])
try await client.contacts.allow(addresses: [wantedConvo.peerAddress, wantedConvo.peerAddress])
try await client.contacts.deny(addresses: [spamConvo.peerAddress, unwantedConvo.peerAddress])
await client.allowContact(wantedConvo.address);
await client.denyContact(spamConvo.address);
await client.contacts.allow([wantedConvo.peerAddress, wantedConvo.peerAddress]);
await client.contacts.deny([spamConvo.peerAddress, unwantedConvo.peerAddress]);
Refresh the consent list
To ensure that you’re using the latest consent preferences, make sure to refresh the consent list from the network. Perform the refresh just in case the consent preference has changed on a different device, for example.
refreshConsentList()returns the history of all consent entries.
- JavaScript
- React
- Kotlin
- Swift
- Dart
- React Native
await client.contacts.refreshConsentList();
import { useEffect } from "react";
import { useConsent } from "@xmtp/react-sdk";
function ConsentList() {
const { refreshConsentList } = useConsent();
useEffect(() => {
void refreshConsentList();
}, []);
// ... UI rendering
}
client.contacts.refreshConsentList()
try await client.contacts.refreshConsentList()
await client.refreshContactConsentPreferences();
await client.contacts.refreshConsentList();
Get the consent list
Load the consent list from a specific time. If no time is specified, it loads the consent list from the last time the refresh was made.
- JavaScript
- React
- Kotlin
- Swift
- Dart
- React Native
await client.contacts.loadConsentList(/* Optional: lastSyncedDate */);
import { useEffect } from "react";
import { useConsent } from "@xmtp/react-sdk";
function LoadConsentList() {
const { loadConsentList } = useConsent();
useEffect(() => {
void (loadConsentList(/* Optional: lastSyncedDate */));
}, []);
// ... UI rendering
}
client.contacts.consentList
try await client.contacts.consentList
var consents = client.exportContactConsents();
await client.contacts.consentList();
Check if a contact is denied or allowed
Call the following methods to check if a contact is denied or allowed.
- JavaScript
- React
- Kotlin
- Swift
- Dart
- React Native
// from the client
const isAllowed = client.contacts.isAllowed(address);
const isDenied = client.contacts.isDenied(address);
// from a conversation
const isAllowed = conversation.isAllowed;
const isDenied = conversation.isDenied;
import { useConsent } from "@xmtp/react-sdk";
function CheckConsent({ conversation }) {
const { isAllowed, isDenied } = useConsent();
useEffect(() => {
const checkConsent = async () => {
const allowed = await isAllowed(conversation.peerAddress);
const blocked = await isDenied(conversation.peerAddress);
// Use `allowed` and `blocked` for UI updates or logic
};
checkConsent();
}, [conversation.peerAddress]);
// ... UI rendering based on consent status
}
client.contacts.isAllowed(wantedConvo.peerAddress)
client.contacts.isDenied(spamConvo.peerAddress)
await client.contacts.isAllowed(wantedConvo.peerAddress)
await client.contacts.isDenied(spamConvo.peerAddress)
var state = client.checkContactConsent(wantedConvo.address);
//state can be ContactConsent.deny, ContactConsent.unkown or ContactConsent.allow
await client.contacts.isAllowed(wantedConvo.peerAddress);
await client.contacts.isDenied(spamConvo.peerAddress);
Get a conversation’s consent preference
When loading a list of conversations, take into account its consent preference. You can get the consentState directly from the conversation.
- JavaScript
- React
- Kotlin
- Swift
- Dart
- React Native
// from the client
const consentState = client.contacts.consentState(peerAddress);
// from a conversation
const consentState = conversation.consentState;
// consentState can be 'allowed', 'denied', or 'unknown'
import { useConsent } from "@xmtp/react-sdk";
function ConversationConsent({ conversation }) {
const { consentState } = useConsent();
const state = consentState(conversation.peerAddress);
// state can be 'allowed', 'denied', or 'unknown'
// ... UI rendering based on the state
}
val state = conversation.consentState()
if (state == ConsentState.DENIED) {
// hide the conversation
}
let state = await conversation.consentState()
if (state == .denied) {
// hide the conversation
}
The user consent feature for Dart hasn't been implemented yet
const state = await conversation.consentState();
if (state === "denied") {
// hide the conversation
}
Streaming the consent list
This section provides an example of how to stream the consent list. The code snippet below demonstrates how to create a new conversation and then stream the consent list, logging each action to the console.
- JavaScript
- React
- Kotlin
- Swift
- Dart
- React Native
const aliceStream = await aliceClient.contacts.streamConsentList();
for await (const action of aliceStream) {
// Each action indicates the address and if it's allowed or denied
}
await aliceStream.return();
import { useStreamConsentList } from "@xmtp/react-sdk";
function ConsentListStreamer() {
const handleAction = (action) => {
console.log("New action received:", action);
// You can update your UI or state based on the action here
};
const handleError = (error) => {
console.error("Error in streaming consent list:", error);
// Handle error state in UI
};
const { error } = useStreamConsentList(handleAction, handleError);
return (
<div>
<h3>Consent List Stream</h3>
{error && <p>Error: {error.message}</p>}
{/* Additional UI for showing streaming status or actions */}
</div>
);
}
export default ConsentListStreamer;
Code sample coming soon
Code sample coming soon
Code sample coming soon
Code sample coming soon
Synchronize user consent preferences
All apps that use the user consent feature must adhere to the logic described in this section to keep the consent list on the network synchronized with local app user consent preferences, and vice versa.
Do not update the consent list on the network except in the scenarios described below.
Update a consent preference in the consent list on the network in the following scenarios only:
A user explicitly denies a contact. For example, the user blocks, unsubscribes from, or disables notifications for the contact. The app should update the consent preference in the consent list to
denied.A user explicitly allows a contact. For example, the user allows, subscribes to, or enables notifications for the contact. The app should update the consent preference in the consent list to
allowed.An existing conversation has an
unknownconsent preference, but a legacy consent preference in the local database exists. The app should update the consent preference in the consent list to match the legacy local content preference.An existing conversation has an
unknownconsent preference, but has an existing response from the user. The app should update the consent preference in the consent list toallowed.
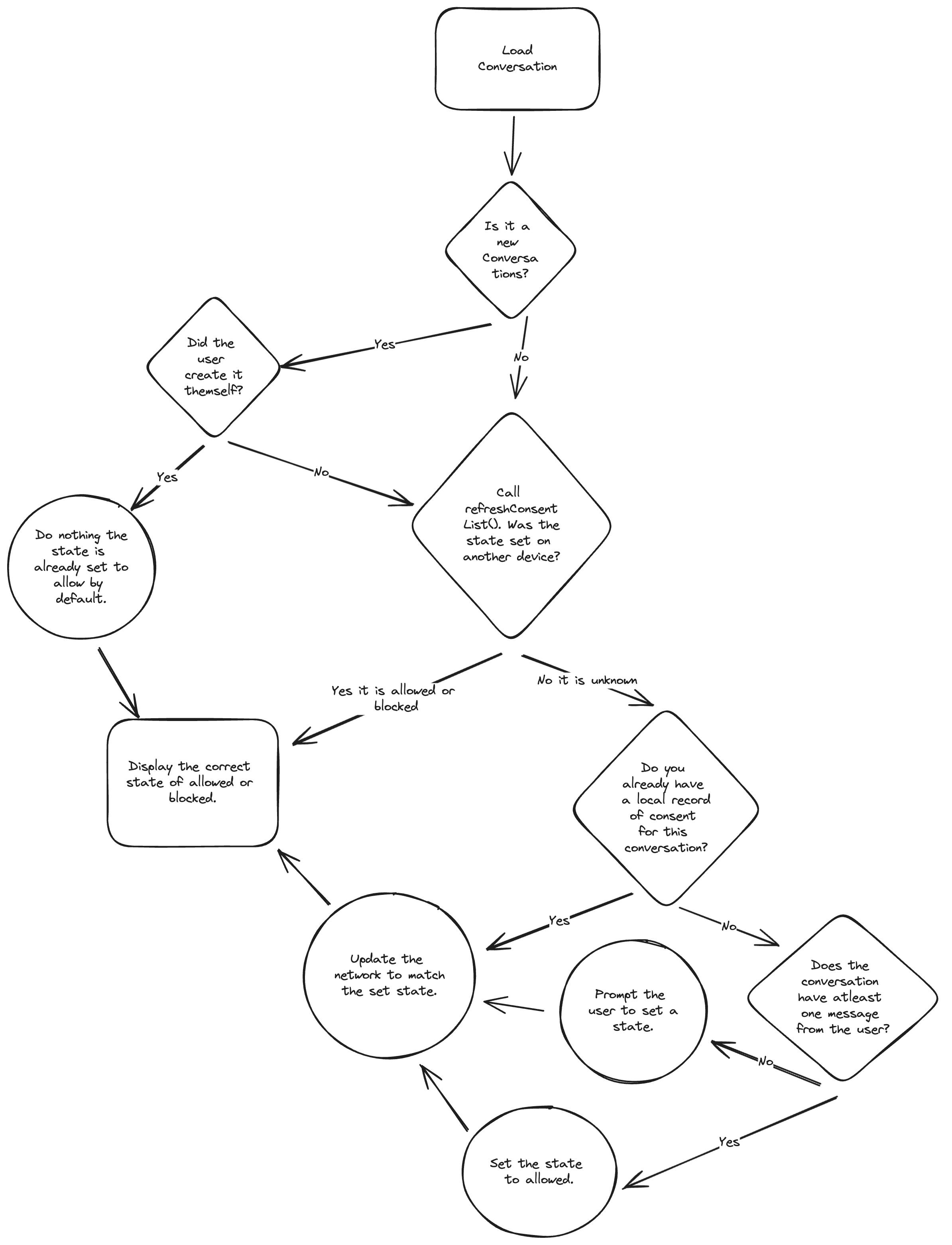
The following diagram illustrates the detailed logic for how user consent preferences are set in an app and in the consent list on the XMTP network.
Tutorials
For practical examples, see these tutorials:
- Enable subscribers with XMTP
- Broadcast messages with XMTP
- Add consent to an existing XMTP inbox JS
- Add consent to an existing XMTP inbox RN
Example repos
- JS example repo xmtp-inbox-portable-consent
- React Native example repo xmtp-inbox-portable-consent

